
Spring IoC是Spring的核心,所以IoC也是Spring MVC的基础,Spring MVC 会建立起一个IOC容器体系,IoC的启动过程与web容器启动的过程是集成在一起的,它们的启动由ContextLoaderListener监听器负责完成。建立IOC容器体系后,DispatcherServlet作为Spring MVC处理web请求的转发器也建立起来,从而完成响应HTTP请求的准备工作。
一、IOC容器的启动(ContextLoaderListener)
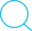
IoC容器的启动过程就是建立上下文的过程,由ContextLoaderListener启动的上下文为根上下文,在根上下文的基础上,还有一个与Web MVC相关的上下文作为根上下文的子上下文来保存DispatcherServlet所需要的MVC对象,构成一个上下文体系。这个上下文体系的建立与初始化是由ContextLoader来完成的。
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
在ContextLoaderListener中实现了ServletContextListener接口,这个接口里的函数会结合Web容器的生命周期被调用(contextInitialized,服务器启动时被调用;contextDestroyed,服务器关闭时被调用)。因为ServletContextListener是ServletContext的监听者,如果ServletContext发生变化,会触发预先设计好的动作,比如初始化和销毁。比如初始化:
ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
//初始化WebApplicationContext根上下文
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//根上下文作为唯一实例存在,用ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE标志位来实现
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
if (this.context == null) {
//创建根上下文
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
//转型为需要产生的IoC容器
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 载入根上下文的双亲上下文
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//设置ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE标志位
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
//判断使用什么样的类作为Web容器中的IoC容器
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
//如果在ServletContext中配置了CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM,则使用这个class反射生成根上下文实例。
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {//如果没有配置CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM,则使用默认的contextClass来反射生成根上下文实例。
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
//设置ServletContext以及配置各类参数,最终调用refresh方法来初始化容器
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
ContextLoaderListener初始化根上下文过程图

二、Spring MVC的启动(DispatcherServlet)
在完成ContextLoaderListener的初始化后,Web容器开始初始化DispatcherServlet。DispatcherServlet会建立自己的上下文来持有Spring MVC的Bean对象,在建立自己持有的IOC容器时,会将根上下文作为自己持有的上下文的双亲上下文,建立了这个上下文后将该上下文保存到ServletContext中,供以后检索和使用。DispatcherServlet的启动过程也就是Spring MVC的启动过程。
2.1 DispatcherServlet的继承关系

DispatcherServlet通过继承FrameworkServlet和HttpServletBean来继承HttpServlet,这样就可以使用Servlet API来对HTTP请求进行响应,成为Spring MVC的前端处理器。
DispatcherServlet的工作分为两部分:一个是初始化部分,通过调用initStrategies方法完成Spring MVC的初始化;一个是对HTTP请求进行响应,作为一个servlet,Web容器会调用Servlet的doGet和doPost方法来完成响应动作。
2.2 DispatcherServlet的启动与初始化
DispatcherServlet的启动与Servlet的启动是相似的,在Servlet初始化时会调用init方法,在DispatcherServlet的基类HttpServletBean的初始化也由init开始。DispatcherServlet持有一个以自己的Servlet名称命名的IoC容器,这个容器作为根上下文的子上下文存在,在Web容器的上下文体系中,一个根上下文可以作为多个Servlet子上下文的双亲上下文。
一般情况下controller相关的bean或者对应的注解扫描配置在子上下文中,而service、dao的bean或者对应的注解扫描配置在根上下文中。
建立MVC的上下文代码逻辑:
HttpServletBean.init()
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// 获取Servlet的初始化参数,配置Bean属性
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
// 具体初始化过程
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//初始化上下文
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
//这里的初始化上下文和ContextLoaderListner不太一样
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//使用ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE来获取根上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 设置根上下文为双亲上下文
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
//如果以上都没有能获取MVC的IoC容器,则创建一个
if (wac == null) {
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
//把建立好的子上下文存放到ServletContext中去,使用的属性名就是当前servlet名
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//实例化需要的具体上下文对象,这个上下文对象也是XmlWebApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
//设置双亲上下文
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + "/" + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
//通过refresh方法来调用容器初始化过程
wac.refresh();
}
DispatcherServlet.onRefresh
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
//启动整个Spring MVC框架的初始化
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
MVC框架的初始化是在initStrategies方法中完成的,初始化了支持国际化的LocaleResolver、request映射的HandlerMappings、视图生成的ViewResolvers等。
//初始化HandlerMapping
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
//detectAllHandlerMappings这里默认为true,即默认从所有的IoC容器中获取HandlerMapping
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {//否则从当前的IoC容器中通过getBean获取所有Bean名称为“handlerMapping”的HandlerMapping
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// 如果没有handlerMappings,则从配置文件中读取
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
initHandlerMappings是对HandlerMappings的初始化,这些Map的作用是为HTTP请求找到相应的Controller控制器,以完成功能逻辑。IoC容器初始化后,容器里有各种各样的Bean,initHandlerMappings会从IoC容器中通过getBean来获取handlerMapping,handlerMapping包含了MVC中Controller的定义和配置,同时handlerMappings变量就已经获取了在BeanDefinition配置好的映射关系。加载的HandlerMapping被放在一个List中并已经排好序,存储着HTTP请求对应的映射数据,List中的一个元素就是一个HandlerMapping,一个mapping中有一系列的URL与Controller的映射。
initHandlerMappings方法调用栈


2.3 MVC处理HTTP分发请求
上面已经完成了HandlerMapping的加载,每一个HandlerMapping持有一系列从URL请求到Controller的映射,这种映射关系通常用一个Map(LinkedHashMap,命名为handlerMap)来持有。
private final Map<String, Object> urlMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
某个URL映射到哪个Controller,这部分的配置是在容器对Bean进行依赖注入时发生的,通过Bean的postProcessor来完成,(registerHandler方法)。这样就为DispatcherServlet的分发奠定了数据基础。
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping注册handler的代码逻辑
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping.initApplicationContext
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
super.initApplicationContext();
registerHandlers(this.urlMap);
}
protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("Neither 'urlMap' nor 'mappings' set on SimpleUrlHandlerMapping");
}
else {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : urlMap.entrySet()) {
String url = entry.getKey();
Object handler = entry.getValue();
// 确保url以"/"开头
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// 去掉空格
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
}
}
}
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
if (getApplicationContext().isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
//如果url是“/”,则这个url映射的Controller就是rootHandler
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}//如果url是“/*”,则这个url映射的Controller就是DefaultHandler
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {//如果url是正常的url,设置handlerMap的key和value分别对应url和对应的Controller
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped URL path [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
}
准备好handlerMap中的数据后,我们来看看handlerMapping如何完成请求的映射处理。 在HandlerMapping中定义了getHandler方法,这个方法会根据我们刚刚初始化得到的handlerMap来获取与HTTP请求对应的HandlerExecutionChain,它封装了具体的Controller对象。HandlerExecutionChain有两个比较重要:拦截器(Interceptor)链和handler对象,handler对象就是HTTP对应的Controller,通过拦截器链里的拦截器来对handler对象提供功能的增强。
AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandler
@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取request对应的handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
//获取默认的handler
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// 根据名称取出对应的Handler Bean
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//把这个handler封装到HandlerExecutionChain中并加上拦截器
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
获取request对应的handler的代码逻辑
@Override
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//从request获取url路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//从HandlerMap中获取指定url路径的handler
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
// 如果没有对应url路径的handler则返回相应的handler(RootHandler或DefaultHandler)
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
}
protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 直接匹配url
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (handler != null) {
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(handler, request);
return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null);
}
// 如果直接匹配url不成功,则匹配最佳的
List<String> matchingPatterns = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String registeredPattern : this.handlerMap.keySet()) {
if (getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern, urlPath)) {
matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern);
}
else if (useTrailingSlashMatch()) {
if (!registeredPattern.endsWith("/") && getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern + "/", urlPath)) {
matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern +"/");
}
}
}
String bestPatternMatch = null;
Comparator<String> patternComparator = getPathMatcher().getPatternComparator(urlPath);
if (!matchingPatterns.isEmpty()) {
Collections.sort(matchingPatterns, patternComparator);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Matching patterns for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + matchingPatterns);
}
bestPatternMatch = matchingPatterns.get(0);
}
if (bestPatternMatch != null) {
handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestPatternMatch);
if (handler == null) {
Assert.isTrue(bestPatternMatch.endsWith("/"));
handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestPatternMatch.substring(0, bestPatternMatch.length() - 1));
}
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(handler, request);
String pathWithinMapping = getPathMatcher().extractPathWithinPattern(bestPatternMatch, urlPath);
Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
for (String matchingPattern : matchingPatterns) {
if (patternComparator.compare(bestPatternMatch, matchingPattern) == 0) {
Map<String, String> vars = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(matchingPattern, urlPath);
Map<String, String> decodedVars = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, vars);
uriTemplateVariables.putAll(decodedVars);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("URI Template variables for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + uriTemplateVariables);
}
return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, bestPatternMatch, pathWithinMapping, uriTemplateVariables);
}
return null;
}
得到handler对象后,把这个handler封装到HandlerExecutionChain中并加上拦截器
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
现在我们完成了对HandlerExecutionChain的封装工作,为handler对http请求响应做好了准备。
DispatcherServlet是HttpServlet的子类,和其他的HttpServlet一样,通过doService方法来响应HTTP请求(再调用doDispatch)。DispatcherServlet通过getHandler得到一个HandlerExecutionChain后,通过HandlerAdapter来验证这个handler的合法性(handler instanceof Controller,如果是Controller的对象则返回true,反之返回false),合法后执行handler方法获取结果数据,这些数据都封装在ModelAndView中返回给前端进行视图呈现,对视图呈现的处理是通过调用入口:render方法来实现的。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}

参考文献:
《Spring技术内幕 深入解析Spring架构与设计原理》